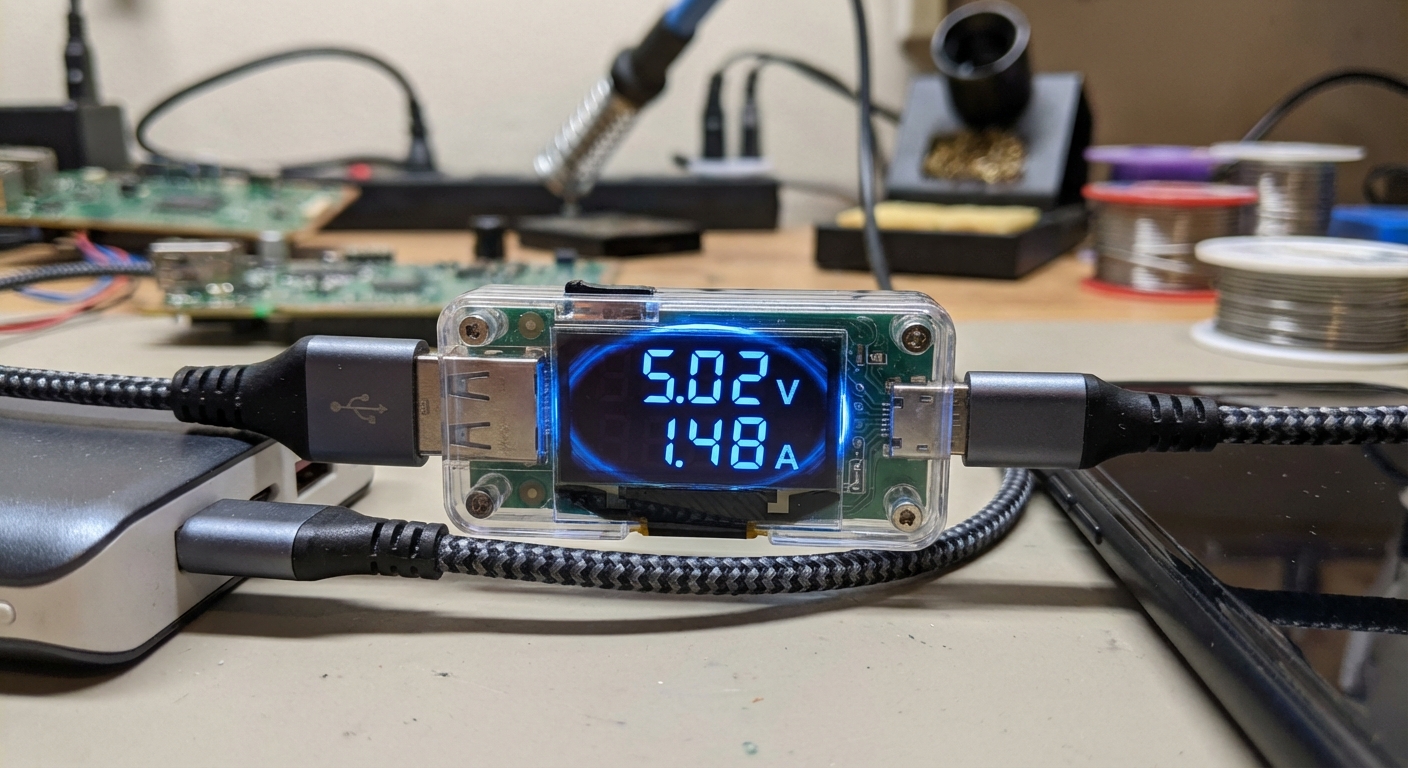
How to Test a USB Port With a Multimeter
Testing a USB port with a multimeter is a practical skill that comes in handy when you’re dealing with faulty or unresponsive USB connections. Whether you’re trying to troubleshoot a device that isn’t charging or determine if a USB port is delivering the correct voltage, understanding how to test these components can save you time and money. The common misconception is that USB ports always require specialized USB testers, while a standard multimeter can effectively measure the voltage and current flowing through a USB port. In this article, you’ll learn how to properly use a multimeter to diagnose USB port issues and ensure your devices are receiving the power they need.
Understanding USB Power Specifications
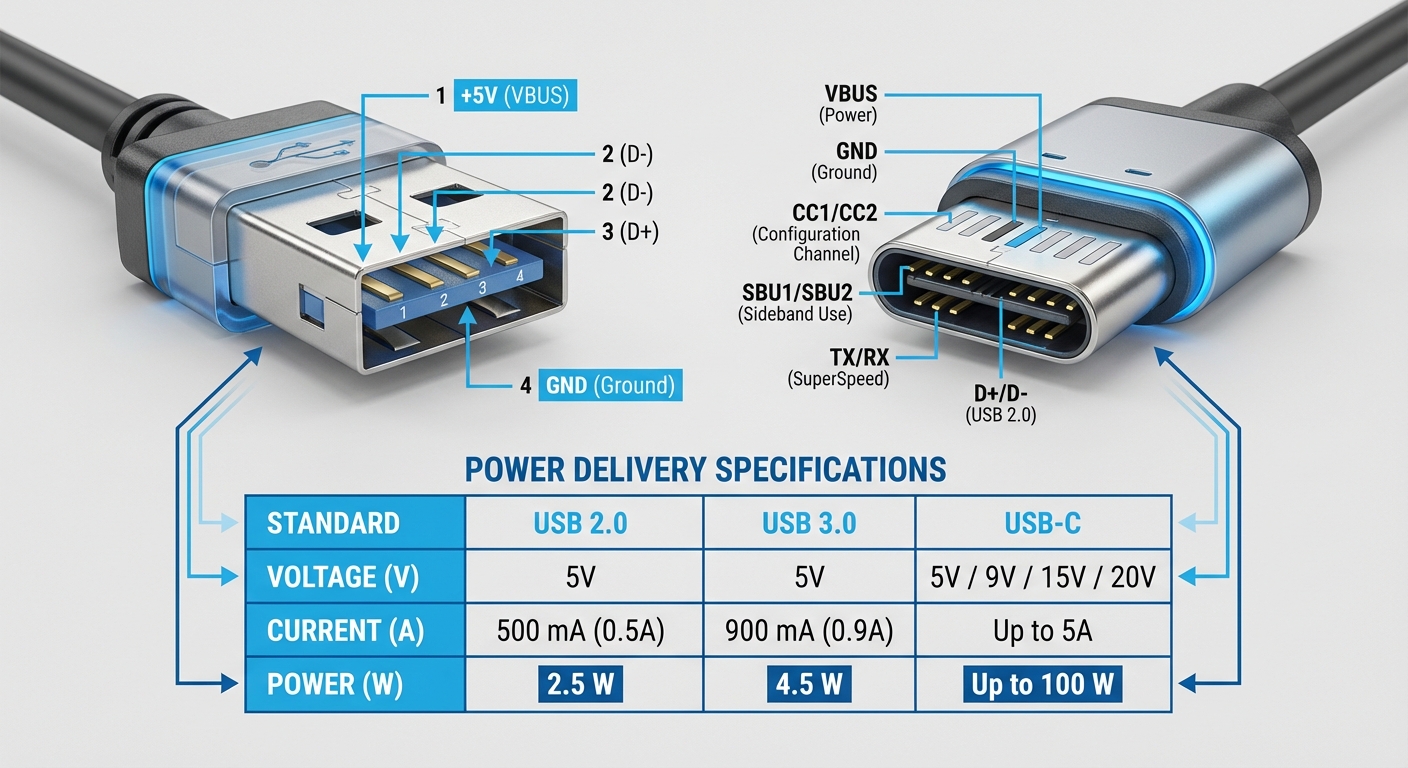
USB ports have standardized power specifications, primarily delivering 5 volts (V) DC. However, different USB versions (USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and USB-C) can provide different levels of current (measured in amperes, A). Recognizing these specifications is crucial for accurate testing:
- USB 2.0: Typically delivers up to 500mA (0.5A).
- USB 3.0: Can supply up to 900mA (0.9A).
- USB-C: Supports higher currents, commonly up to 3A or more, depending on the device and cable.
With this knowledge, you can approach your testing with the right expectations based on the type of USB port you’re using.
Essential Tools for Testing a USB Port
To test a USB port, you will need:
- A digital multimeter (DMM).
- A USB device or cable to test.
If you prefer more specialized testing, you can use a USB multimeter. These devices are designed to measure voltage and current simultaneously and can often display additional statistics like power consumption.
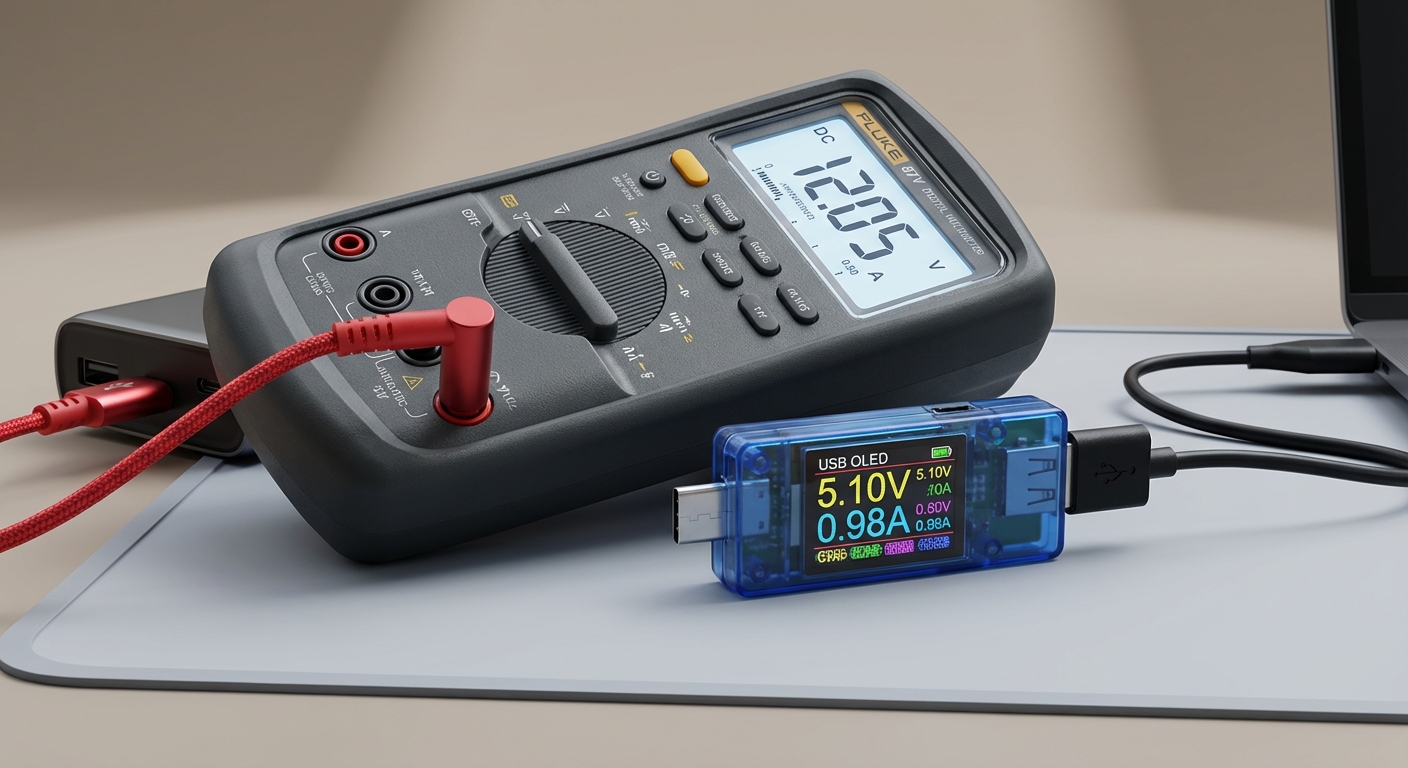
Steps to Measure USB Port Voltage Using a Multimeter
Measuring the voltage across the USB ports involves a few straightforward steps:
- Set up your multimeter: Turn on your digital multimeter and set it to measure DC voltage (usually represented by the V— symbol).
- Insert the probes: Carefully insert the black probe into the COM (common) port and the red probe into the VΩmA port of the multimeter.
- Test the USB port: Insert the USB connector into the port being tested. With the probes, touch the metal part inside the USB connector: the red probe to the +5V pin (usually the first pin), and the black probe to the GND pin (the fourth pin).
- Read the measurement: Check the multimeter display for the voltage reading. It should read approximately +5V.
Steps to Measure USB Port Current Using a Multimeter
To measure the current, the multimeter has to be placed in series with the load. Here are the steps:
- Prepare your multimeter: Switch the multimeter to measure current (A). Choose the correct current range depending on your expected value.
- Connect a load: To measure current, you need to connect a load (such as a resistor) between the USB power line and ground. This will draw current from the USB port.
- Probe placement: Disconnect the wire from the load, and connect one probe to the wire and the other probe to the load’s input. This creates a series circuit.
- Take the measurement: Power on the circuit and read the current value displayed on the multimeter.
Note: Be cautious with the resistor value to avoid drawing excessive current. A common resistor value to use is around 10 ohms.
Common Issues When Testing USB Ports
While testing, you may encounter several common issues:
- Incorrect readings: This may occur due to improper probe placement. Ensure that you’re connecting to the correct pins.
- Non-functioning ports: If a USB port does not deliver expected voltage or current, it may be damaged or malfunctioning. Consider checking the hardware or using a different port.
- Compatibility issues: Make sure your multimeter can handle the operating ranges for the tests you are performing. Some models have lower limits that might affect readings.
Using a USB Multimeter
USB multimeters combine features of a conventional multimeter with specialized capabilities for testing USB connections. They can display voltage and current simultaneously and may include additional diagnostic data such as power consumption and the health of the USB connection. To use a USB multimeter:

- Plug the USB multimeter into the port: Connect the USB multimeter to the port you want to test.
- Connect your device: Insert the USB cable of the device you wish to test into the multimeter.
- Read the data: Observe the readings on the multimeter display, which typically shows voltage, current, and sometimes additional information like power (Watts).
Common Misconceptions About Testing USB Ports
It is often believed that:
- Only specialized USB testers can measure voltage and current accurately.
- All problems with USB ports stem from faulty cables or devices, disregarding port functionality.
Understanding that a standard multimeter can provide accurate readings allows for effective troubleshooting without needing extensive equipment.
Conclusion
Testing a USB port with a multimeter can provide valuable insights into its functionality and performance. By following the simple steps outlined above, you can diagnose issues, determine power delivery, and ensure that your devices are receiving the appropriate voltage and current. Whether it’s a charging issue or a data transfer problem, having the knowledge to test USB ports can facilitate effective troubleshooting. For related topics, consider exploring how to choose the right USB cables for your devices.
FAQ
Q: How do I know which pins to measure on a USB port?
A: The first pin on a standard USB connector is usually +5V, while the fourth pin is GND (ground). Make sure to reference the USB pinout diagram for accurate identification.
Q: Can I damage my devices by testing a USB port with a multimeter?
A: If used correctly, a multimeter should not damage your devices. However, applying excessive current while measuring could potentially harm the components.
Q: Do I need to disconnect anything when testing a USB port?
A: For voltage measurement, the device can remain connected. For current measurement, you must break the circuit by disconnecting the load to place the multimeter in series.
Q: What should I do if the voltage is lower than expected?
A: Check the physical connections, try a different USB port, or test the device with another charger or cable to rule out faulty hardware.
Q: Will a USB multimeter be more accurate than a standard multimeter?
A: USB multimeters are specialized for USB testing and can provide additional insights and convenience, but a standard multimeter can still yield accurate voltage and current readings if correctly applied.
Rotating USB



