USB Type C Pinout Brief Diagram.
What is USB Type-C

USB-C, or USB Type-C, is a modern way to connect devices. It’s super fast and can handle both data transfer and charging. With USB-C, you can move data at speeds up to 10 gigabits per second and charge devices with up to 100 watts of power. This makes it perfect for all kinds of gadgets, like laptops, smartphones, and accessories. USB-C is popular because it’s easy to use, works with tons of devices, and makes charging and data sharing quicker and more efficient.
USB-C Features Explained Simply
USB-C is packed with features that make it super convenient and powerful for connecting devices. From its easy-to-use plug to its ability to handle data, video, and charging, here’s a simple breakdown of what makes USB-C so awesome.
Flippable Connector
The USB-C plug is designed to be user-friendly because you can plug it in either way—no flipping it over to get it right! Unlike older USB plugs that only worked one way, USB-C’s symmetrical shape makes connecting quick and hassle-free. This also means less wear and tear on the plug and port, so they last longer.
Works with Lots of Standards
USB-C is like a Swiss Army knife for connections—it can handle all sorts of data and video needs. Here’s what it can do:
- USB 2.0: Moves data at up to 480 Mbps, great for basic file transfers or connecting things like keyboards.
- USB 3.0: Speeds up to 5 Gbps for faster data, like copying big files.
- USB 3.1 Gen 2: Even faster at 10 Gbps, perfect for editing high-quality videos.
USB-C can also do more than just USB stuff, thanks to Alternate Mode. For example:
- DisplayPort: Lets you connect to monitors or TVs to show video and audio, cutting down on extra cables.
- HDMI: Works with older TVs or monitors that use HDMI, so you don’t need a separate cable.
- Thunderbolt 3: Combines super-fast data (up to 40 Gbps) and video, letting you connect to things like external drives or 4K screens with just one cable.
- MHL (Mobile High-Definition Link): Connects phones or tablets to TVs or projectors, making it easy to show presentations or watch videos on a big screen.
This flexibility means USB-C can handle almost any connection you need, keeping things simple.
Smart Power Delivery
USB-C is great at charging because it can send a lot of power, up to 100 watts! That’s enough to charge laptops, tablets, or smartphones. It uses something called USB Power Delivery (PD) to figure out exactly how much power a device needs. Instead of blasting out a fixed amount of power, USB-C talks to the device to send just the right amount, like 5 volts for a phone or 20 volts for a laptop. This makes charging faster, safer, and more efficient, saving energy and keeping devices from getting too hot.
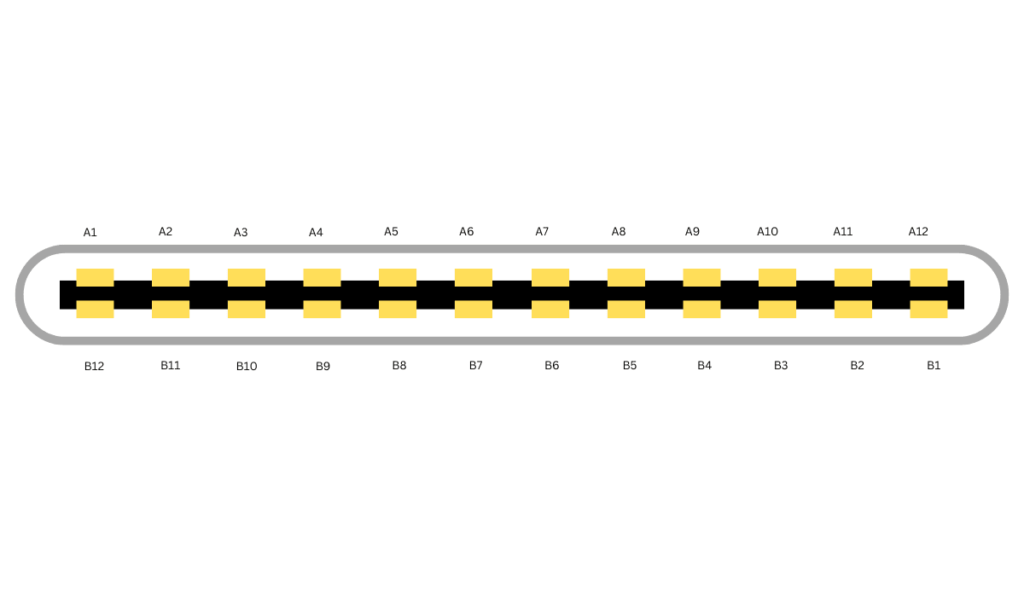
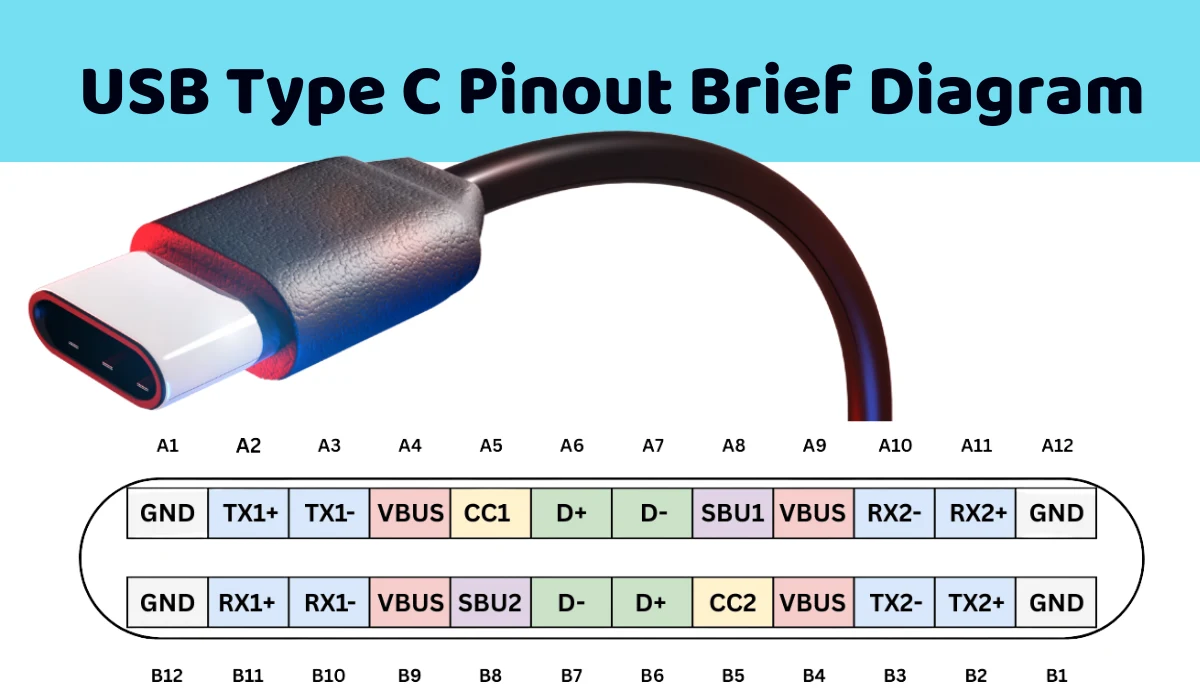
The USB Type-C Receptacle/Plug Pins
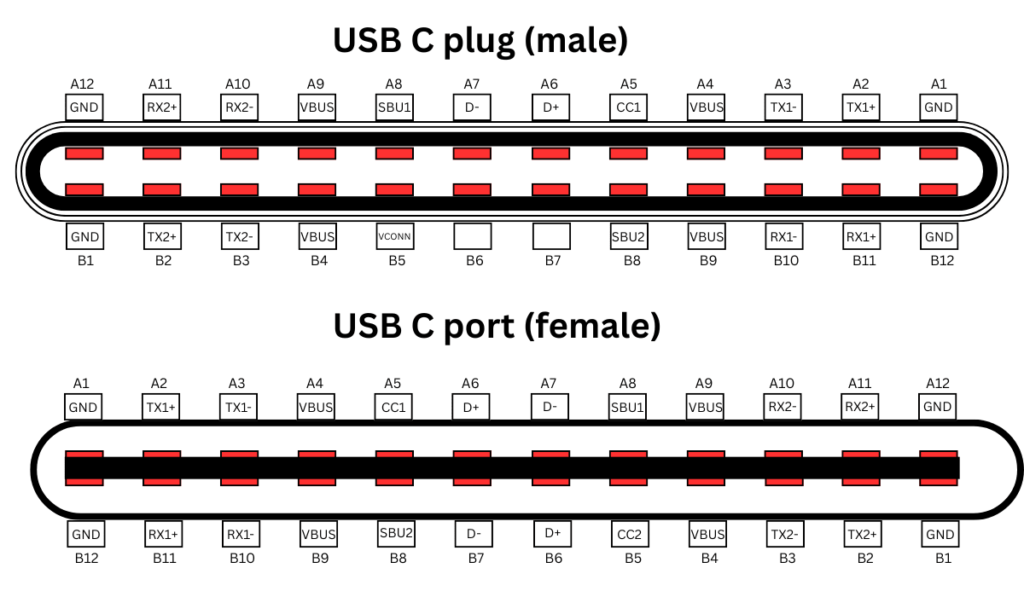
How USB-C Pins Work: A Simple Guide
The USB-C connector is like a tiny powerhouse with 24 pins that make it super versatile. These pins handle everything from fast data transfer to charging big devices like laptops. Let’s break down what these pins do and how they make USB-C so useful, in a way that’s easy to understand.
What the 24 Pins Do
The USB-C connector has 24 pins, each with a specific job:
- 8 pins are for super-fast data transfer, moving files at speeds up to 10 Gbps.
- 4-pin handle power, delivering up to 100 watts (or even 240 watts with newer standards) to charge devices or power things like monitors.
- The rest take care of grounding, communication, and setting up the connection so everything works smoothly.
This setup lets USB-C do a lot—charge your phone, connect to a TV, or transfer huge files—all with one cable.
USB 2.0 Data Pins (D+ and D-)
The D+ and D- pins are key for USB 2.0 data, letting devices share info like files or commands. In a USB-C port, there are two sets of these pins (two D+ and two D-). Why two? Because USB-C is flippable—you can plug it in either way, and the extra pins make sure data flows correctly no matter how you insert it. Even though there are two sets, they act like one pair for USB 2.0, keeping data transfers reliable and easy.
USB-C Plug Pinout: What Each Pin Does
The USB-C plug is the part you stick into your device, and its pins make all the magic happen. Here’s a simple look at the main ones:
- Vbus Pins (A1, B1): These carry power. They start at 5 volts but can go up to 20 volts or even 48 volts with Power Delivery (PD), delivering up to 240 watts. That’s enough to charge a laptop or power big devices. The cable and device “talk” to figure out the right power level, so nothing gets overloaded.
- D+ and D- Pins (A6, A7, B6, B7): These handle data for USB 2.0, 3.0, or 3.1 Gen 2, supporting speeds from 480 Mbps to 10 Gbps. They make sure your files move fast and work with older USB devices, too.
- Configuration Channel (CC) Pins (A5, B5): These are like the brains of the connection. They figure out how much power a device needs, decide if it’s sending or receiving power, and set up the connection details. This makes sure everything runs smoothly.
- Sideband Use (SBU) Pins (A2, B2): These help with extra features, like sending video signals for DisplayPort or HDMI when USB-C is used in Alternate Mode. This lets you connect to a monitor or TV without a separate cable.
- Identity (ID) Pins (A4, B4): These tell the device which way the plug is inserted and what’s connected, like an accessory or charger. They also help decide if the device should send or receive power, making connections hassle-free.
- Ground (GND) Pins (A3, B3): These keep everything safe and stable by providing a ground for power and data. Good grounding prevents glitches and keeps your device working properly.
Why This Matters
The USB-C’s 24 pins are what make it so powerful and flexible. Whether you’re charging a laptop, transferring files, or hooking up a monitor, these pins work together to get the job done. The flippable design, smart power delivery, and support for tons of features mean you can do more with just one cable.
Power and Ground Pins

The USB Type-C connector has two important pins for power: VBUS (which supplies power) and GND (which completes the circuit). By default, VBUS provides 5V, but devices can “talk” to each other and agree to increase the voltage up to 20V and current up to 5A. This means USB-C can deliver up to 100W of power—enough to charge big devices like laptops. The best part? It automatically adjusts power based on what the connected device needs, making it super versatile.
The RX and TX Pins

The RX (Receive) and TX (Transmit) pins in USB-C are what make fast data transfer possible, especially in USB 3.0 and 3.1. The USB-C connector has two sets of these pins, so it can send and receive data quickly and efficiently.
A cool thing about USB-C is that it works no matter how you plug it in—upside down or right side up. This is thanks to a smart chip (a multiplexer) that automatically adjusts the connections.
These pins also allow Alternate Mode, which lets USB-C do more than just data, like carrying DisplayPort or HDMI signals for video and audio. Plus, they help with USB Power Delivery (USB PD), so devices can negotiate how much power they need (up to 100W), making it great for charging laptops and other power-hungry gadgets.
In short, these tiny pins make USB-C fast, versatile, and reversible—all at the same time!
The CC1 and CC2 Pins
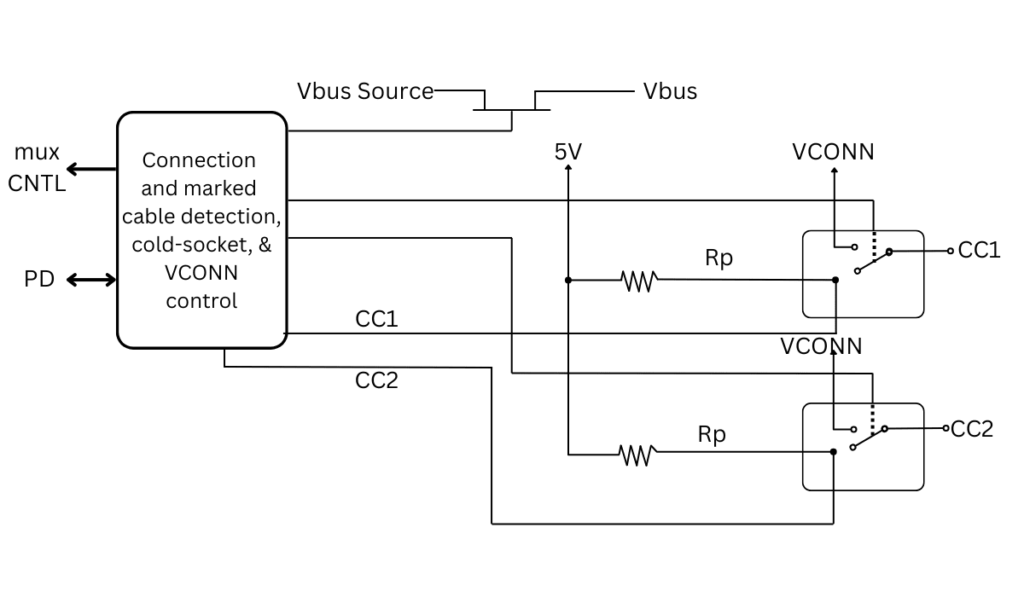
The CC (Channel Configuration) pins in USB-C—CC1 and CC2—are like the “smart assistants” of the connector. Here’s what they do in simple terms:
- Cable Detection & Orientation
- They figure out which way the cable is plugged in, so USB-C works no matter how you insert it—upside down or right side up.
- Power Negotiation
- They help devices talk to each other and agree on how much power can be delivered (like fast charging for phones or laptops).
- This is how USB-C can safely provide up to 100W of power without overheating.
- Alternate Mode Setup
- When you use USB-C for things like video (DisplayPort/HDMI) or super-fast data, the CC pins help switch the port into the right mode.
- Data Communication
- They also help set up the connection for high-speed data transfer when needed.
In short, these tiny pins make sure your USB-C cable charges fast, works both ways, and adapts to whatever you plug into it—whether it’s power, video, or data.
The SBU1 and SBU2 Pins
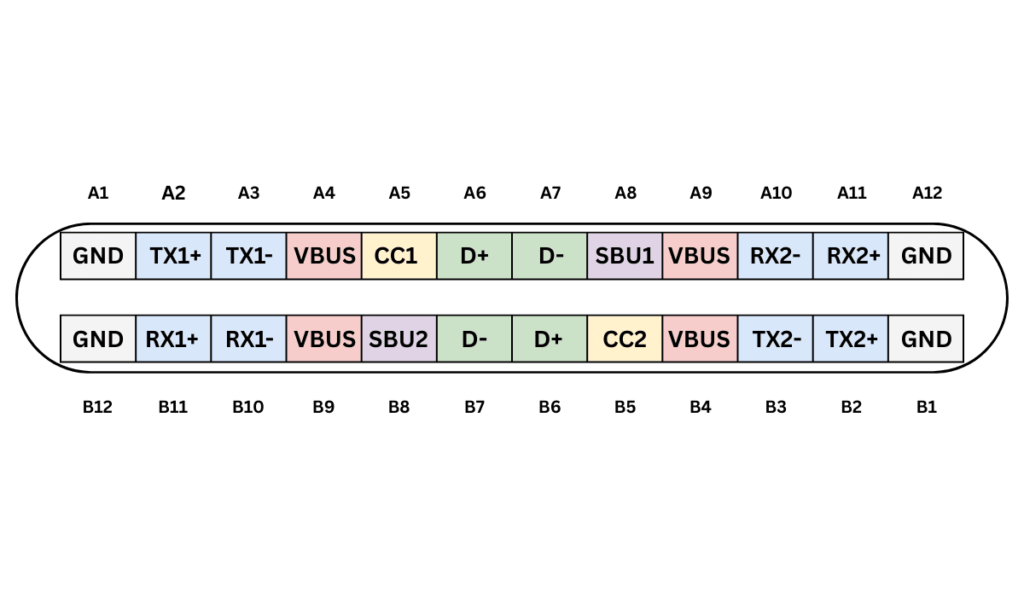
The SBU (Sideband Use) pins—SBU1 and SBU2—are like the “extra helpers” in a USB-C cable.
- They handle low-speed signals and aren’t used for normal USB data.
- Their main job is in Alternate Mode, where USB-C switches to other functions like DisplayPort or HDMI for video output.
- Thanks to these pins, a single USB-C port can do multiple jobs—charging, fast data transfer, and even video—without needing extra ports.
- This makes devices sleeker and simpler, since one USB-C connector can replace several different cables.
In short, SBU pins help USB-C stay versatile and powerful, doing way more than just charging or transferring files!
USB Power Delivery

USB Power Delivery (PD) is like a smart power negotiator for USB-C. Here’s how it works in plain terms:
- Smart Power Handshake
Devices “talk” to each other over the CC wire to agree on the best power level. No more guessing—your phone, laptop, or tablet gets exactly the power it needs. - Flexible Charging for All Devices
It can deliver anywhere from tiny trickles of power (for earbuds) up to 100W (for laptops), adjusting voltage (5V, 9V, 15V, 20V) and current (up to 5A) on the fly. - One Port, Many Jobs
The same USB-C port can: - Charge your phone super fast
- Power a laptop without a bulky charger
- Even send video to a monitor—all at once!
- Safer & Smarter Charging
- Prevents overheating by avoiding overcharging
- Extends battery life by giving just the right power
- Let you swap chargers between devices worry-free
- Power + Data in One Cable
While fast-charging your laptop, you can still transfer files or connect to a display—no extra cables needed.
In short, USB PD turns USB-C into a universal power boss, making charging faster, safer, and way more convenient!
Alternate Modes
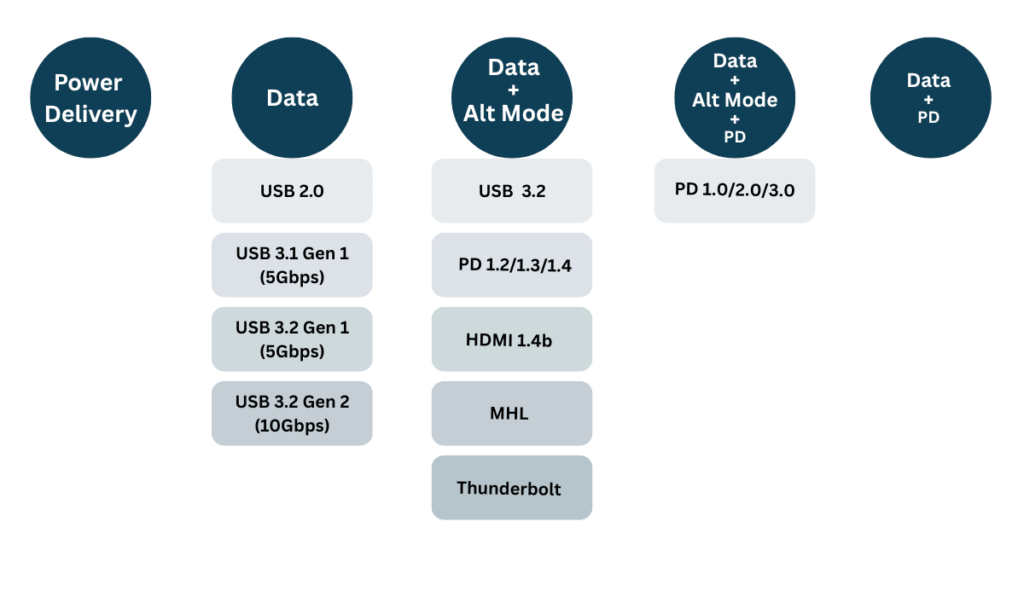
USB-C’s Alternate Modes: One Port to Rule Them All
USB-C’s killer feature? Alternate Modes—letting one tiny port replace multiple connectors. No more juggling different cables or hunting for the right port. Here’s how it works:
1. DisplayPort Mode: For Stunning Video
- Turns USB-C into a high-res video/audio port—no extra DisplayPort needed.
- Supports 8K resolution and smooth high refresh rates.
- Perfect for gamers, video editors, and anyone who needs crisp visuals.
2. MHL Mode: Phone-to-TV Made Easy
- Lets smartphones mirror to TVs/projectors seamlessly.
- Great for streaming movies, sharing photos, or work presentations.
- Saves space—no need for a separate HDMI port on your phone.
3. Thunderbolt Mode: Speed Demon
- Delivers blazing-fast 40Gbps speeds (that’s 4x USB 3.2!).
- Handles heavy-duty tasks like video editing, external GPUs, or giant file transfers.
- Also carries power and video—one cable for everything.
4. HDMI Mode: Plug & Play for TVs/Monitors
- Outputs HD video and audio just like a regular HDMI port.
- Works with home theaters, monitors, and projectors.
- No adapters needed if your display supports USB-C.
Why This Rocks
✅ Fewer ports = thinner, lighter devices (goodbye, bulky laptops!).
✅ One cable for charging, data, and video—no more cable clutter.
✅ Future-proof—supports the latest high-res displays and fast transfers.
With Alternate Modes, USB-C becomes the ultimate universal port—whether you’re gaming, working, or just charging your phone. One connector, endless possibilities. 🔥
Understanding Port Roles: DFP and DRP
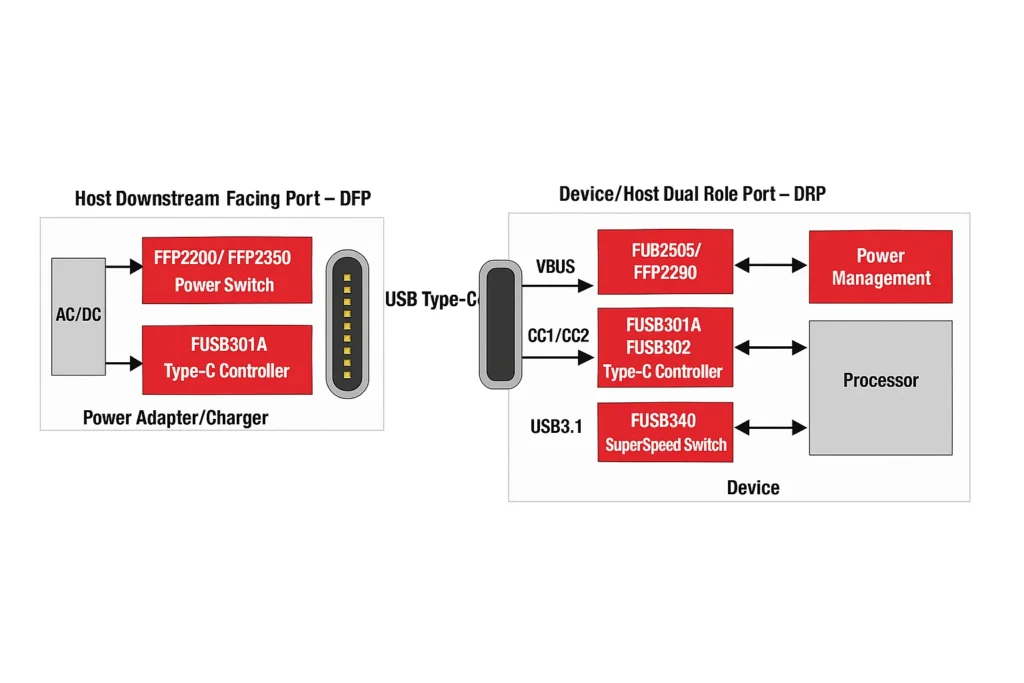
How USB Connections Work: Hosts, Peripherals, and Smart Dual-Role Devices
When you connect two USB devices, they don’t communicate as equals—one takes charge as the host (also called a Downstream Facing Port or DFP), while the other acts as the peripheral.
- The host (like your laptop) controls the connection and supplies power.
- The peripheral (like a flash drive or keyboard) uses that power and follows the host’s commands.
But some devices, like modern smartphones, are flexible—they have Dual-Role Ports (DRP) and can switch roles depending on what’s plugged in:
- Act as a host when connecting to a USB drive or mouse (so you can access files or use peripherals).
- Act as a peripheral when plugged into a computer (to transfer files or charge).
This smart switching makes USB more versatile, letting one port do double duty!
1 thought on “USB Type C Pinout Brief Diagram”