Understanding the 12VHPWR Connector
The 12VHPWR connector, introduced to simplify the power delivery for high-performance graphics cards, can handle up to 600W of power. This is crucial for power-hungry components like Nvidia’s RTX 4090 and the latest RTX 5090. However, an alarming trend emerged in recent years: instances of these connectors melting under load. This article delves into the factors contributing to connector failure, the functionality of the 12VHPWR standard, and the alternatives available for ensuring a safer power delivery system for high-end GPUs.
The Problem: Connector Melting
The melting of 12VHPWR connectors is a pressing issue for users of high-performance graphics cards. Predominantly linked with Nvidia’s RTX 4000 and 5000 series, users have reported failures that can lead to significant hardware damage. This contributes to downtime and may necessitate the replacement of both the GPU and the power supply unit (PSU).
The root of the problem lies not with the power connectors themselves, but with the immense power demands of the latest graphics cards, pushing these connectors to their thermal limits. A common misconception is that simply using a higher gauge connector will provide a fail-safe solution. However, this misconception overlooks the complexity involved in power transmission and thermal management.
In this article, readers will learn about the engineering behind the 12VHPWR connector, why users are experiencing melting issues, the implications of using alternative connectors, and how to choose a power delivery solution that minimizes risk.
How the 12VHPWR Connector Works
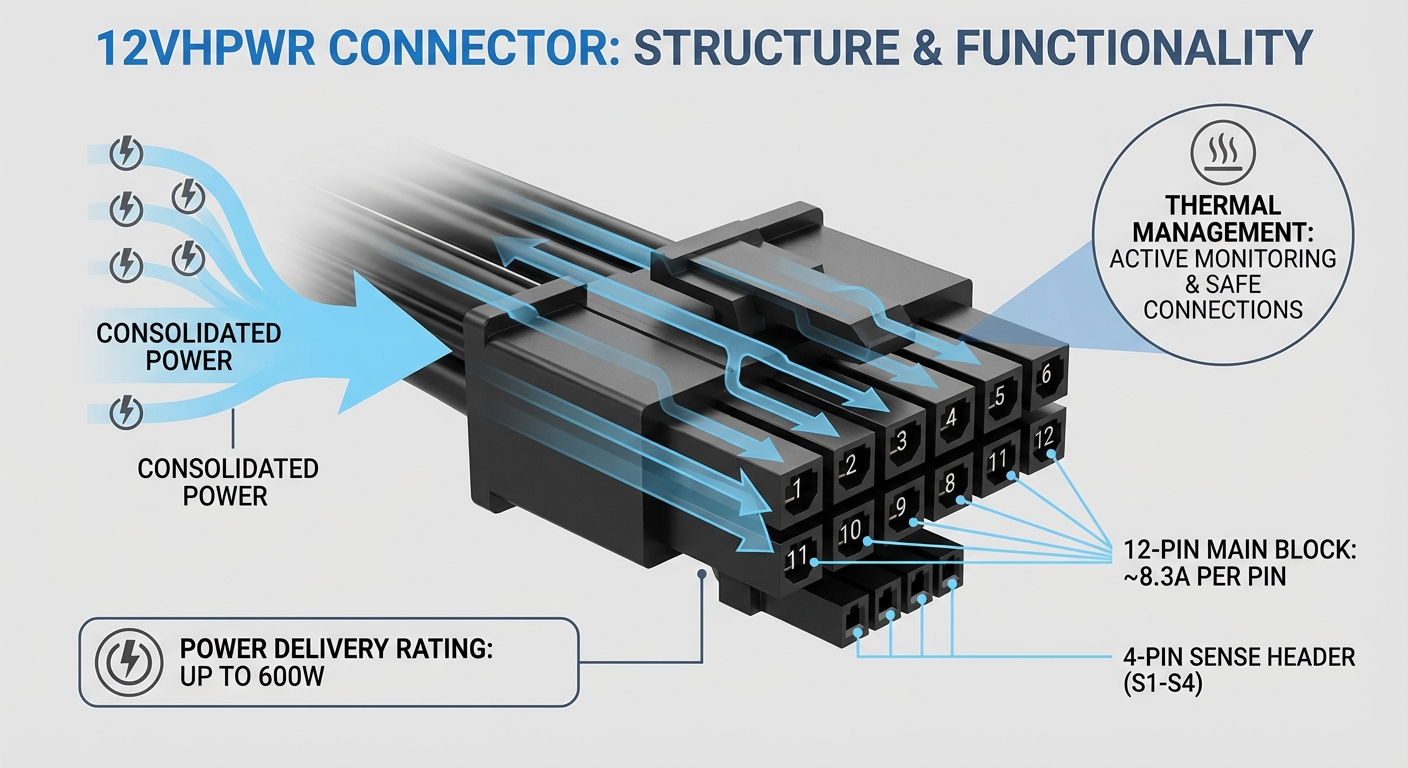
The 12VHPWR (12 Volt High Power) connector was designed to offer a more streamlined solution for high-performance graphics cards, reducing cable clutter by consolidating multiple power connections into a single unit. Here’s how it functions:
- Power Delivery: The connector can supply up to 600W by utilizing multiple wire paths, typically split across a 12-pin configuration.
- Current Rating: At 600W, each pin has to safely manage around 8.3A, which is well within the capabilities of standard 16AWG wires, which are known to handle such currents effectively.
- Heat Management: While the standard itself is capable of handling significant loads, issues arise when temperatures exceed safe limits due to inadequate cooling or poor contact at connection points.
Reasons Behind the Melting Issue
Despite the theoretical capacity of the 12VHPWR connector, real-world applications reveal several factors contributing to melting:
- High Power Draw: With GPUs like the RTX 5090 drawing up to 575W, even connectors designed for high loads struggle under continuous heavy operation.
- Poor Contact: A frequent cause of overheating connectors is poor contact at the connection points—any physical gaps or corrosion can increase resistance, leading to excessive heat.
- Thermal Runaway: If the connector heats up beyond its rated temperature, the plastic housing can begin to deform and eventually melt, leading to failure.
Comparative Analysis: 12VHPWR vs. Traditional Connectors
While newer power connectors are designed for efficiency, traditional connectors like the 8-pin Molex provide a more robust option in certain scenarios:
| Feature | 12VHPWR Connector | 8-Pin Molex Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Max Power Delivery | 600W | 150W (per connector) |
| Number of Pins | 12 | 8 |
| Melting Risk | Higher | Lower |
| Cable Management | Improved | Cluttered |
Alternatives for High-Power Systems
Given the challenges with the 12VHPWR connector, users may seek alternatives to mitigate risks:
- Multiple 8-Pin Connectors: Using several 8-pin Molex connectors can distribute the load more evenly across multiple connections, potentially reducing overheating.
- Upgraded PSU: Investing in a high-quality PSU with better cooling capabilities can help maintain safe operating temperatures for connectors under load.
- Thermal Monitoring: Some users may benefit from installing thermal monitoring software or hardware to track temperatures in real-time and prevent overheating.
User Experiences and Insights
User feedback on forums and review sites has uncovered a range of experiences that emphasize the importance of addressing these issues proactively. Some users report switching back to traditional connectors due to recurring melting incidents with high GPU power demands.
It has also been noted that differences in manufacturing quality between GPUs and cables can lead to inconsistencies in performance, with some makes and models experiencing fewer issues than others. Thus, careful selection of components and manufacturer reputation can play a pivotal role.
FAQs
Q: What causes the 12VHPWR connectors to melt?
A: The primary causes include high power draw, poor contact leading to increased resistance, and inadequate heat management.
Q: Are all 12VHPWR connectors prone to melting?
A: While they are designed for high power delivery, variations in manufacturing quality and installation can lead to different failure rates.
Q: Can I prevent melting connectors?
A: Yes, by ensuring good connection quality, using alternative connectors such as 8-pin Molex, and monitoring temperatures.
Q: What are the signs of a failing connector?
A: Signs include excessive heat, discoloration, or visible melting of the connector housing.
Q: Should I return my melting connector to the manufacturer?
A: Yes, if your connector is melting, contact the manufacturer for a replacement or further support.
Conclusion
In summary, the 12VHPWR connector is an innovative solution for power delivery in high-performance graphics cards but is not without its drawbacks. Users experiencing melting issues must consider alternatives and maintain best practices to ensure safe operation. As graphics card demands continue to rise, it is essential to stay informed about power delivery solutions and potential risks. Explore related topics on power supply design and connector standards for a comprehensive understanding.
Rotating USB



