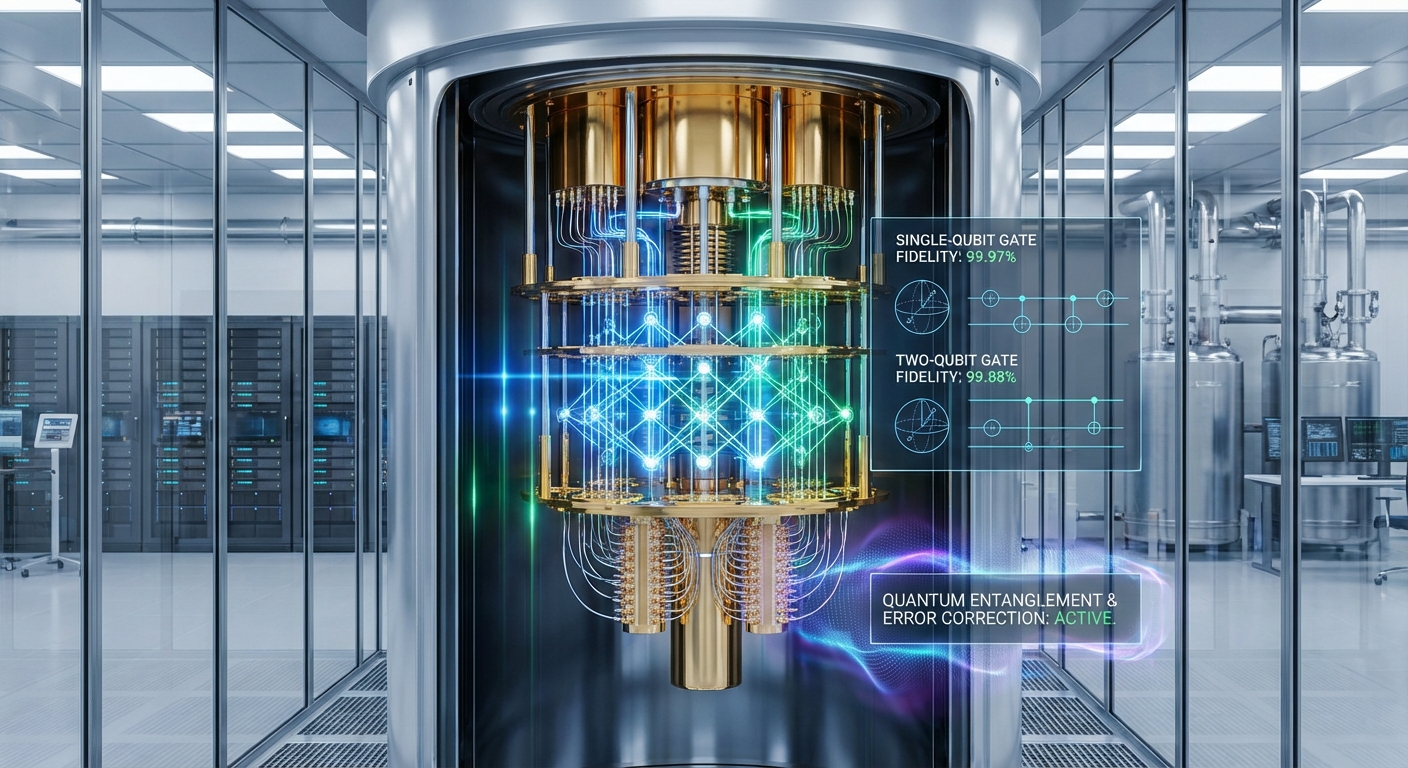
Introduction
The emergence of quantum computing brings forth unprecedented advancements in computation, enabling tasks that were previously unimaginable. A key component in achieving practical quantum computing is the fidelity of quantum gates, which directly influences the reliability and efficiency of quantum operations. This article addresses the fidelity numbers associated with Google’s Willow quantum chip, uncovering what makes it a noteworthy development in the field. Understanding these fidelity metrics is vital, as they signal the chip’s reliability in executing complex quantum algorithms. A common misconception is that all quantum chips have similar performance levels, but this is far from the truth. Readers will learn about Willow’s impressive fidelity numbers, how they compare to existing technologies, and the implications for future quantum computing developments.
Understanding Quantum Gate Fidelity
Quantum gate fidelity refers to the accuracy with which quantum gates perform operations on qubits. In quantum computing, each operation can be thought of as a gate which manipulates qubits. High fidelity is crucial because it signifies that the operations will yield results close to ideal conditions, essential for the effectiveness of quantum algorithms.
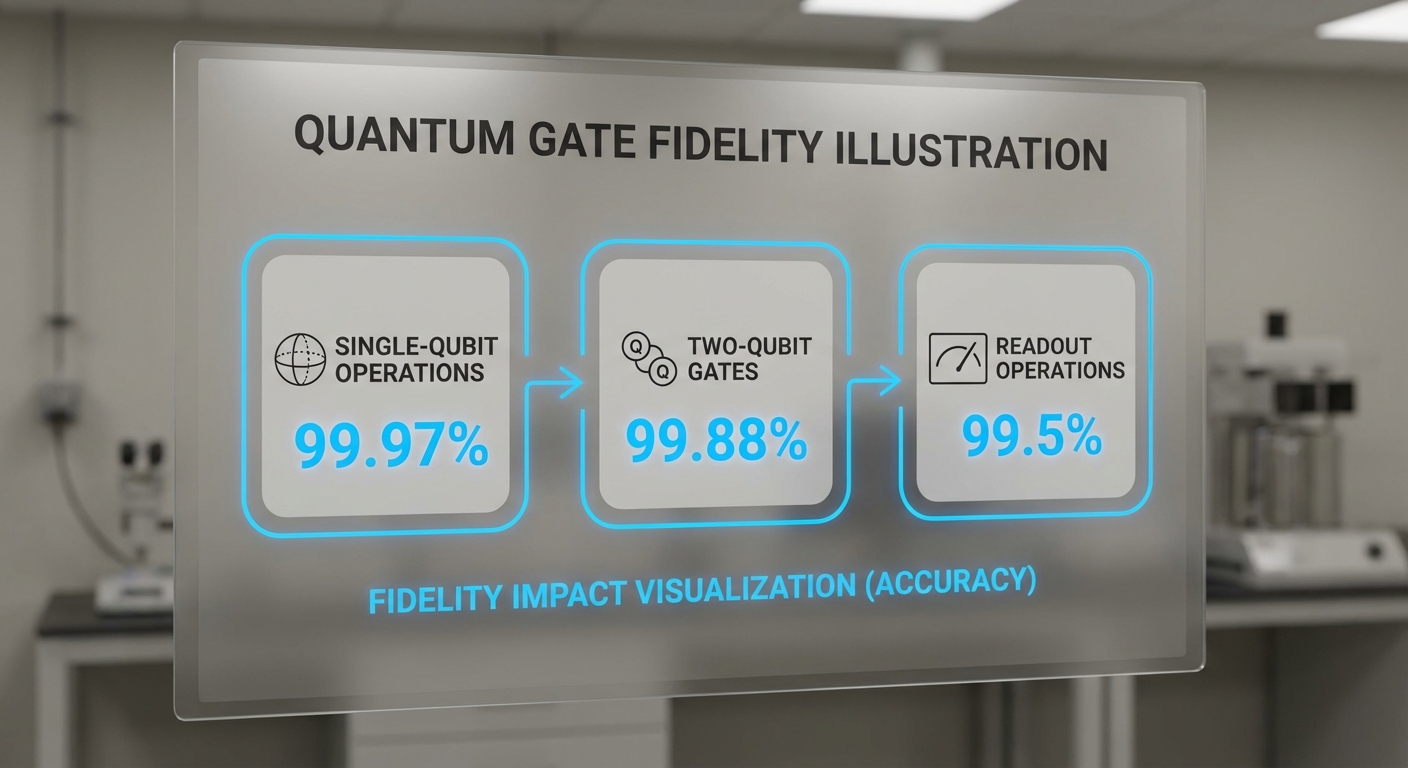
How Quantum Gates Work
Quantum gates are the building blocks of quantum circuits, analogous to classical logic gates. They operate on quantum bits (qubits) and can perform various operations, such as flipping the state of a qubit (single-qubit gates) or entangling two qubits (two-qubit gates). Fidelity measures how accurately these gates enact the intended transformations.
Key Metrics of Willow’s Quantum Gates
Willow has demonstrated remarkable performance in terms of quantum gate fidelity:
- Single-Qubit Operations: 99.97% fidelity, indicating extremely reliable operations with minimal error.
- Two-Qubit Entangling Gates: 99.88% fidelity, showcasing strong performance in creating quantum entanglement.
- Readout Operations: 99.5% fidelity, essential for accurately measuring qubit states.
The Importance of High Fidelity
High fidelity in quantum operations directly impacts quantum error correction and the reliability of a quantum computer. Errors in quantum computations often arise from decoherence and other noise, making error correction vital in scaling up quantum technology.
Quantum Error Correction
Quantum error correction (QEC) involves techniques that help maintain the integrity of quantum information. Willow contributes significantly to this field by bridging the gap between existing error correction protocols and practical implementation.
- Single-Qubit Gate Error: 0.035% ± 0.029%, a mean value for simultaneous operations.
- Two-Qubit Gate Error: 0.33% ± 0.18% for controlled-Z (CZ) gates, demonstrating high accuracy in entangling operations.
- Measurement Error: 0.77% ± 0.21%, essential for ensuring that output results reflect true qubit states.
Performance Benchmarks
Willow’s performance has been validated through rigorous benchmarking, specifically using Random Circuit Sampling (RCS) to assess its computational capabilities against classical computing resources. Notably, as the number of qubits increases, the reduction of computational errors enhances the quantum characteristics of the system.
Execution Speed and Capabilities
Willow exhibits impressive execution speeds:
- Error Correction Cycles: 909,000 cycles per second, enabling rapid real-time error correction.
- Random Circuit Sampling Execution: Achieves 63,000 circuit repetitions per second on chip, further demonstrating speed advantages.
Comparative Analysis with Previous Chips
Comparing Willow with its predecessor Sycamore reveals substantial progress:
| Metric | Willow | Sycamore |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Qubits | 105 | 53 |
| Single-Qubit Gate Fidelity | 99.97% | 99.85% |
| Two-Qubit Gate Fidelity | 99.88% | Unspecified (lower) |
| Measurement Error | 0.77% ± 0.21% | Unspecified (higher) |
Critical Implications for Quantum Computing
The advancements represented by Willow mark a significant step toward scalable, fault-tolerant quantum computation. As highlighted in various studies, achieving high fidelity numbers is crucial for practical quantum applications and advancing quantum error correction techniques.
Broader Impact on Quantum Technologies
The implications of Willow’s performance can extend to numerous fields, including quantum cryptography, complex molecular simulations, and machine learning. High fidelity will facilitate deeper explorations into quantum materials and algorithms that may revolutionize industries.
FAQ
Q: What is quantum gate fidelity?
A: Quantum gate fidelity measures the accuracy with which a quantum gate operates, signifying how close the output is to the intended result.
Q: Why is high fidelity important in quantum computing?
A: High fidelity ensures that quantum operations are reliable, which is essential for error correction and overall computational success.
Q: How does Willow compare to previous quantum chips?
A: Willow substantially improves upon previous quantum chips like Sycamore, with higher fidelity rates and a greater number of qubits.
Q: What are quantum error correction cycles?
A: Quantum error correction cycles are processes used to detect and correct errors in quantum computations, improving the reliability of operations.
Q: How does Random Circuit Sampling assess quantum performance?
A: Random Circuit Sampling is a benchmark employed to evaluate a quantum processor’s performance, particularly its ability to execute complex quantum circuits accurately.
Conclusion
In summary, Google’s Willow quantum chip demonstrates exceptional gate fidelity numbers that are critical for advancing quantum computing technologies. With single-qubit fidelity of 99.97% and significant improvements in two-qubit operations, Willow paves the way for robust quantum systems capable of tackling complex real-world problems. This progress underscores the shift toward larger-scale, error-correcting quantum computers that will likely reshape various fields of research and industry.
For more information on quantum computing principles, you can visit Wikipedia.
Rotating USB