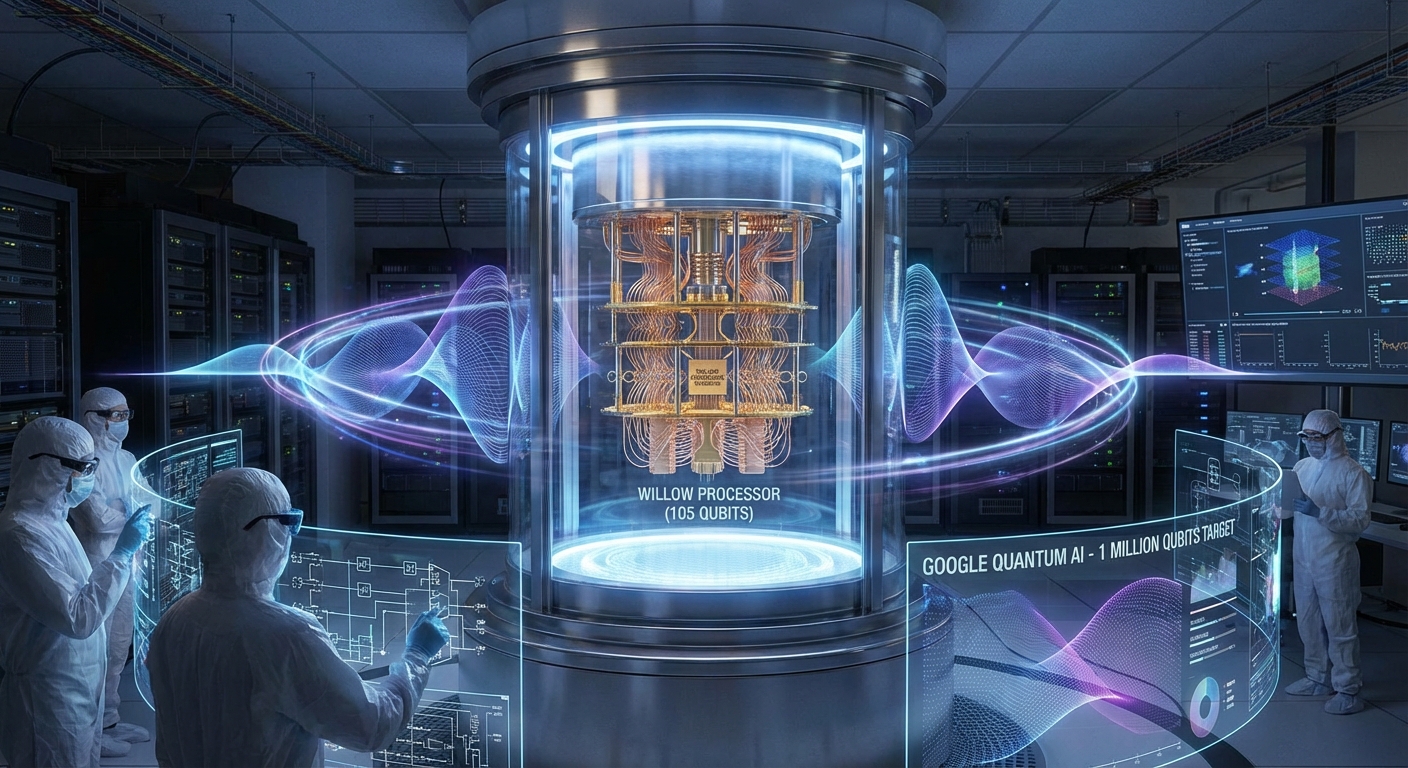
Introduction
Google’s announcement regarding its 105-qubit Willow quantum processor has marked a significant milestone in the ongoing quest for scalable quantum computing. This article explores how Google plans to scale Willow to an ambitious target of one million qubits, a figure critical for breaking modern encryption and achieving practical quantum advantage. The move towards such a vast number of qubits may seem daunting, but it highlights the potential of quantum technologies to solve problems currently beyond classical computation. A common misconception is that simply increasing the number of qubits leads to better performance; however, issues like error rates and qubit coherence times must also be addressed. By diving into the advancements of the Willow chip and Google’s strategic roadmap, readers will gain insight into the complexities of scaling quantum computing and the future of this transformative technology.
Understanding Quantum Computing and Qubits
Quantum computing fundamentally differs from classical computing by utilizing qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to the principles of quantum superposition. This ability allows quantum computers to process vast amounts of information more efficiently. However, achieving scalability in quantum computing is not just about increasing the number of qubits; it requires improving error rates and implementing effective quantum error correction mechanisms. Google’s Willow chip, with its current 105 qubits, serves as a testbed to explore these possibilities.
The Current State of Google’s Willow Processor
Willow is recognized for its contributions to error correction and achieving a significant reduction in error rates as qubit counts increase. This exponential reduction is crucial because it paves the way for constructing logical qubits that can operate below the critical error correction threshold. Google reported that Willow could complete computations in under five minutes that would take supercomputers 10 septillion years to accomplish, thus demonstrating its potential for solving complex problems more efficiently.
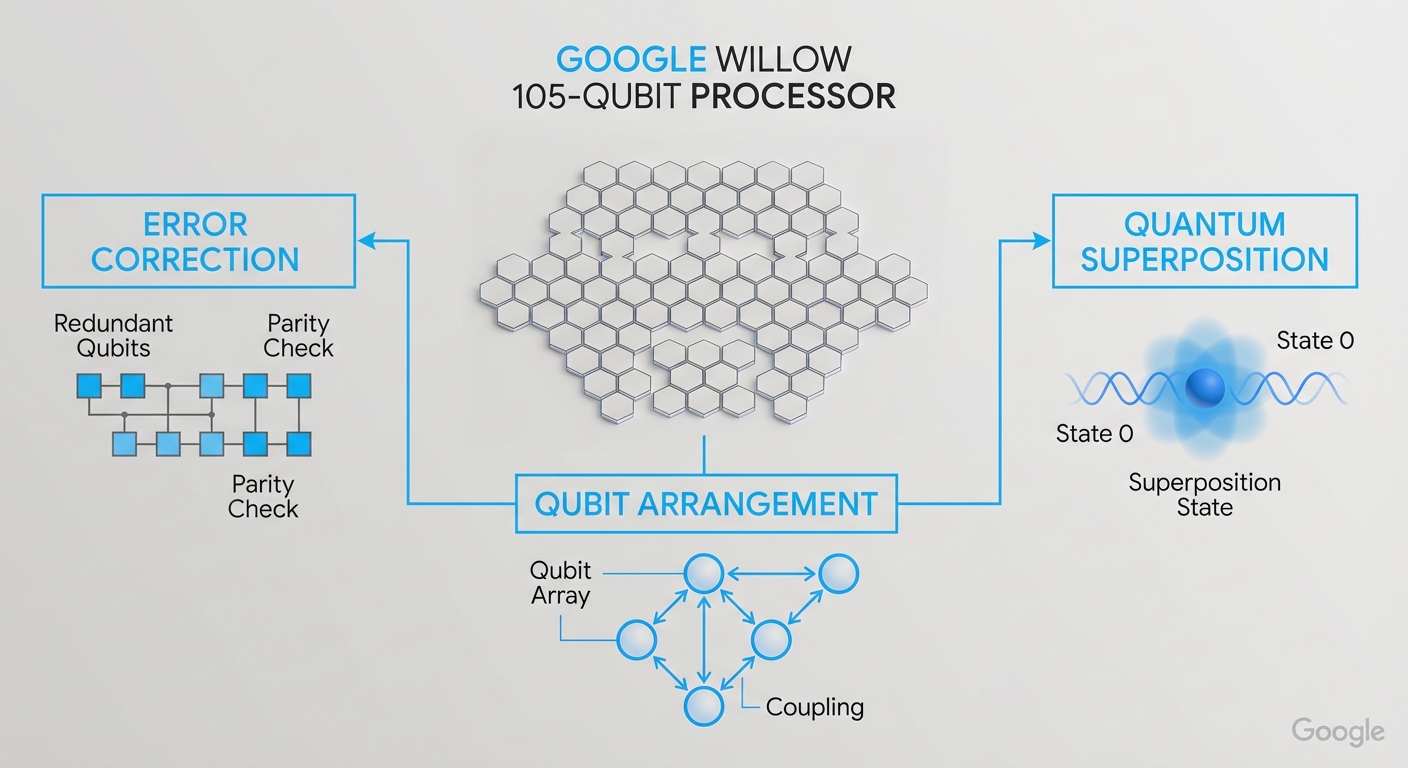
The Path to One Million Qubits
The objective of scaling Willow to one million qubits presents several challenges and considerations:
- Infrastructure and Design: New designs will be necessary to house the vast number of qubits while maintaining coherence and minimizing error rates.
- Quantum Error Correction: Developing robust error correction algorithms that can function effectively at scale will be vital. Willow’s current advancements provide a foundation for this future work.
- Material Science: Innovations in materials used for qubit fabrication will help enhance performance and reliability at larger scales.
- Integration with Classical Computing: A hybrid approach that combines classical and quantum computing resources may be the key to practical applications.
Lessons from Previous Milestones
To contextualize the advancements, it’s helpful to compare Willow with earlier technologies. Google’s Sycamore chip, which achieved quantum supremacy with 53 qubits, served as the stepping stone upon which Willow was built. The lessons learned from programming and calibrating Sycamore directly informed the design and operation of Willow, underscoring the iterative nature of quantum technology development.
Pioneering Quantum Advantage
With an exponential increase in computational capabilities, Google’s Willow chip is a clear step toward achieving quantum advantage—a state where quantum computers can perform tasks beyond the reach of classical supercomputers. The pivotal moment in this journey was when Willow executed a random circuit sampling benchmark successfully, a test previously accomplished by the Sycamore chip. This demonstrates that not only is Google advancing the number of qubits but also enhancing the real-world applicability of quantum computing solutions.
Implications for Security and Beyond
The estimated one million qubits will be necessary for breaking modern encryption methods, posing both opportunities and challenges. As quantum computing evolves, the cybersecurity landscape will shift significantly, necessitating adaptations in encryption technologies to safeguard sensitive information. This transition also has profound implications for various industries, including finance, healthcare, and logistics, where secure communication channels are essential.
Future Considerations and Challenges
As Google pursues its goal of scaling Willow to one million qubits, the company must navigate numerous technical hurdles:
- Cooling Technologies: Quantum processors operate at near absolute zero temperatures. Innovations in cooling methods will be necessary to support larger qubit counts.
- Qubit Coherence Time: Maintaining the integrity of qubits over time continues to be a key area of research. Effective solutions will enable longer operations without decoherence.
- Scalability of Quantum Algorithms: As the hardware progresses, algorithms must also be tailored to leverage the full potential of a million qubits.
Conclusion
Google’s Willow processor serves as a significant milestone in the quest for scalable quantum computing, exhibiting major advancements that set the stage for future developments. Achieving a million qubits involves overcoming substantial engineering, scientific, and practical challenges. As quantum computing continues to evolve, its potential applications across sectors hint at a transformative future that blends classical and quantum methods, promising not only enhanced computational capabilities but also new paradigms for security. These discussions underscore the importance of ongoing research and development efforts in quantum technology.
FAQ
Q1: What is the current number of qubits in Google’s Willow chip?
A1: Google’s Willow chip currently features 105 qubits.
Q2: How does the number of qubits relate to computational power?
A2: More qubits generally increase computational power, but effective error correction and qubit stability are also critical factors.
Q3: What is quantum advantage?
A3: Quantum advantage refers to the ability of a quantum computer to perform tasks that are infeasible for classical computers.
Q4: Why is error correction important in quantum computing?
A4: Error correction is essential to make quantum computations reliable, especially as the number of qubits increases.
Q5: What industries may benefit from advancements in quantum computing?
A5: Industries such as finance, healthcare, cybersecurity, and logistics are expected to experience significant improvements due to quantum computing.